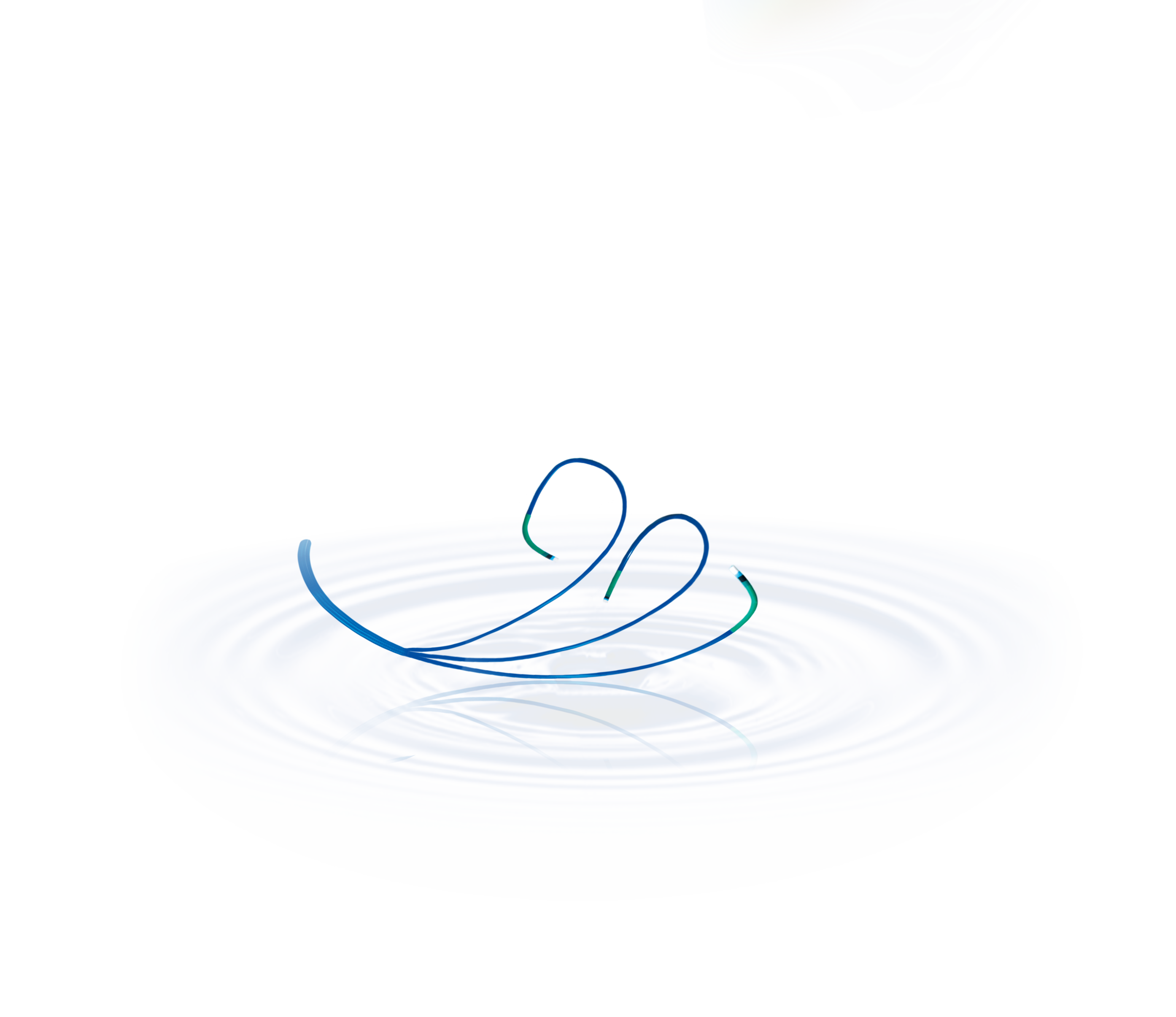
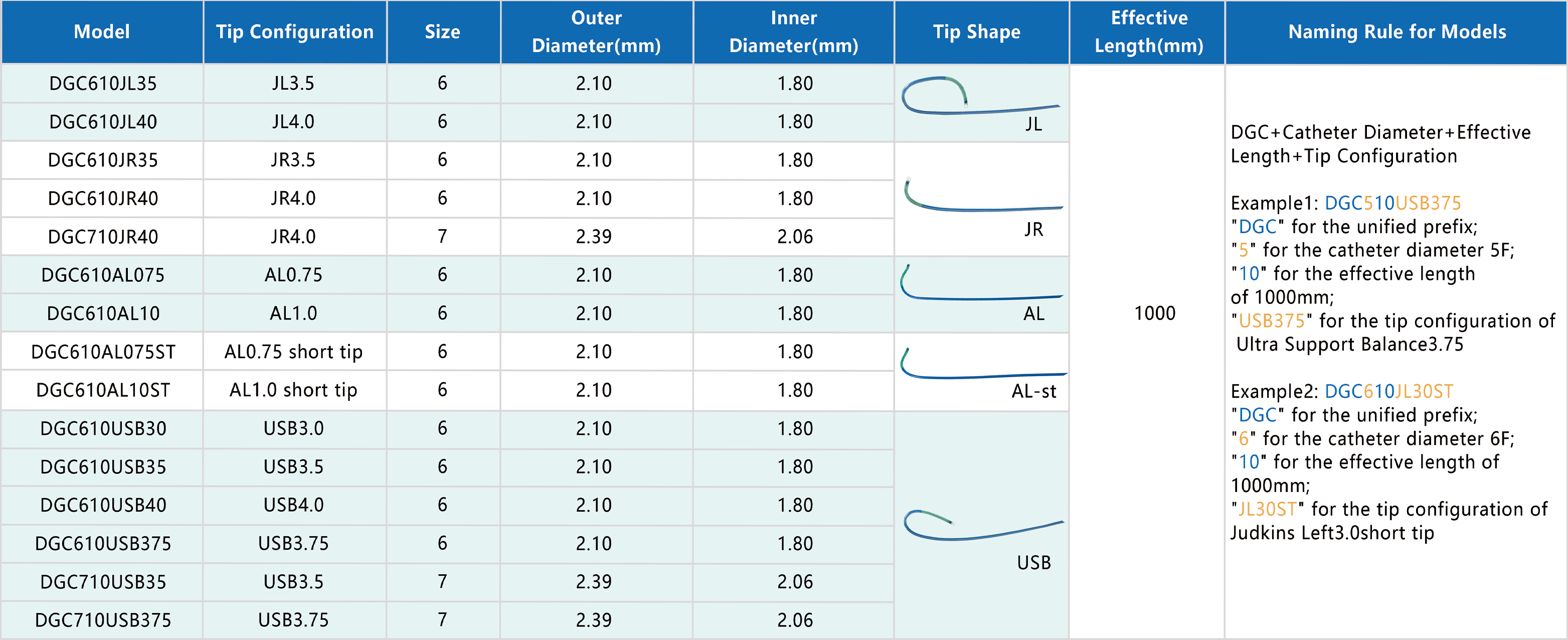
Guiding Catheter
Guiding catheters are typically composed of biocompatible materials such as polyurethane or nylon, chosen for their flexibility, durability, and compatibility with bodily tissues. The catheter shaft is reinforced with braided or coiled wires to provide structural support and torqueability while maintaining flexibility for navigation through tortuous vascular anatomy. Soft, atraumatic tips minimize trauma to blood vessels during insertion and positioning. Radiopaque markers or bands incorporated into the catheter shaft enhance visibility under fluoroscopy or other imaging modalities, allowing for precise navigation and positioning during procedures. Demax’s guiding catheters are engineered with advanced materials and design features to optimize performance and safety, ensuring successful outcomes in a wide range of interventional procedures.
- Soft Tips: The catheter is equipped with soft tips, meticulously designed to provide clear visualization and ensure easy access to target sites within the vasculature. These soft tips minimize trauma to blood vessels during insertion and positioning, enhancing patient comfort and safety.
- Large Chamber: With a large chamber diameter of 1.80 millimeters (mm) for 6 French (F) catheters, the guiding catheter offers excellent compatibility with various consumables used during interventional procedures. This spacious chamber allows for smooth passage of instruments and devices, facilitating seamless procedural workflow and optimizing clinical outcomes.
- Solid Wall Structure: The guiding catheter features a solid wall structure, engineered to provide robust support and enhanced torsion control during navigation through complex vascular anatomy. This structural design ensures stability and reliability, allowing physicians to maneuver the catheter with confidence and precision, even in challenging lesions.
- Good Coaxiality: The catheter exhibits good coaxiality, meeting the need for accessing difficult lesions within the vasculature. This feature enables healthcare professionals to maintain alignment and control over interventional devices, ensuring accurate placement and effective treatment delivery.
- Coronary Angiography and Angioplasty: Guiding catheters are commonly used in coronary interventions to access and navigate through the coronary arteries for diagnostic imaging and treatment of coronary artery disease.
- Peripheral Angiography and Interventions: In peripheral vascular interventions, guiding catheters enable access to arteries and veins in the arms, legs, and other peripheral vessels for diagnostic imaging and therapeutic procedures.
- Neurovascular Interventions: Guiding catheters are utilized in neurointerventional procedures to access and navigate through the cerebral arteries and other intracranial vessels for the treatment of strokes, aneurysms, and other neurovascular disorders.
- Embolization and Ablation: Guiding catheters facilitate the delivery of embolic agents, coils, or ablation devices to target sites within the vasculature for the treatment of vascular malformations, tumors, and other pathological conditions.
- Thrombectomy and Vascular Access: Guiding catheters are employed in thrombectomy procedures to remove blood clots from occluded blood vessels and in vascular access procedures to facilitate the placement of catheters, guidewires, and other intravascular devices.
Related products
-
Tip Forming
Precision Medical Tubing Services Tip Forming involves shaping and forming the tips of medical-grade tubing materials to meet the specific requirements of medical device applications. The composition of the tubing used in this process varies depending on the desired properties and performance characteristics required for the medical device. Typically, medical tubing is made from biocompatible polymers such as polyethylene (PE), polyurethane (PU), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), silicone, or thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). These materials are selected for their flexibility, durability, and compatibility with bodily fluids and tissues.
-
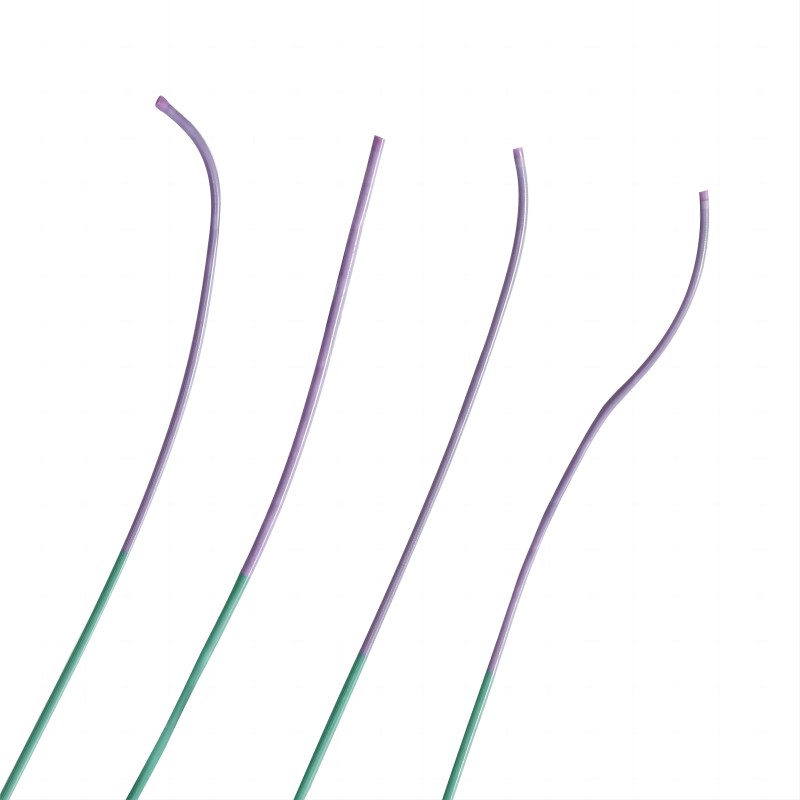
Microcatheter
Features:
1. PTFE inner layer allows for smooth passage for embolic agents;
2. Optimal trackability through tortuous anatomy;
3. Available in pre-shaped tip shape configurations for vessel engagement;
4. Four shapes provides more option for clinical usage;
5. 2.0F/2.2F/2.6F/2.8F models are available;
6. Hydrophilic coating technology, smoothly through the lesion. -
FEP Heat Shrink Tube
The FEP Heat Shrink Tube boasts a composition rooted in fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP), a thermoplastic polymer renowned for its exceptional properties in medical applications.
FEP exhibits a unique combination of characteristics that make it ideally suited for medical tubing. Its molecular structure imparts remarkable clarity to the tubing, allowing for optimal visualization of fluids and instruments during medical procedures, essential for accurate monitoring and precise manipulation.
-
Pebax Tube
Pebax tubing is composed of a blend of thermoplastic elastomers, typically consisting of polyether and polyamide segments. This unique composition imparts Pebax tubing with its distinctive combination of flexibility, durability, and biocompatibility, making it an excellent choice for medical tubing applications.