Endoscopic steerable shafts are important tools in medical procedures. They are used in minimally invasive surgeries to help doctors navigate through the body with precision. Steering capability is essential for accurately guiding the shaft to reach the target area. This helps in reducing damage to surrounding tissues. To improve their performance, these shafts need reinforcement. Braid and coil reinforcements are added to increase strength and flexibility. The Demax Braid & Coil Reinforcement endoscopic steerable shaft is one such device. It is designed to offer better strength and flexibility for different medical uses.
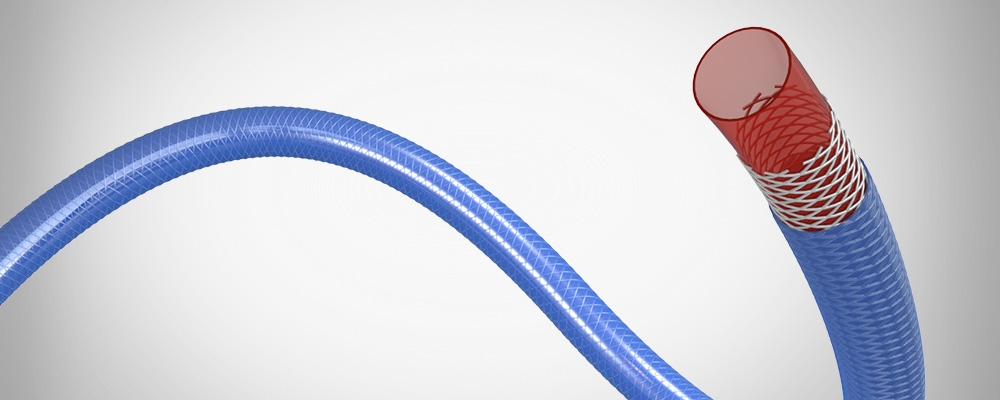
Design and Structure of Endoscopic Steerable Shaft
Basic Components
The endoscopic steerable shaft has several important parts. The outer jacket is made of materials like TPU, Pebax, or PA. These materials help protect the inner components. The steerable core is the main part that controls the movement. It has several layers. The inner layer may include PTFE, TPU, Pebax, or PA. This structure provides high torque and strong operability, making the shaft easy to control during use.
Steering Mechanism
The shaft can be steered using flexible cables or actuation wires. These wires help control the direction of the shaft. When force is applied to the wires, the shaft moves accordingly. This allows precise control in guiding the shaft through the body.
Reinforcement Techniques
Braid Reinforcement
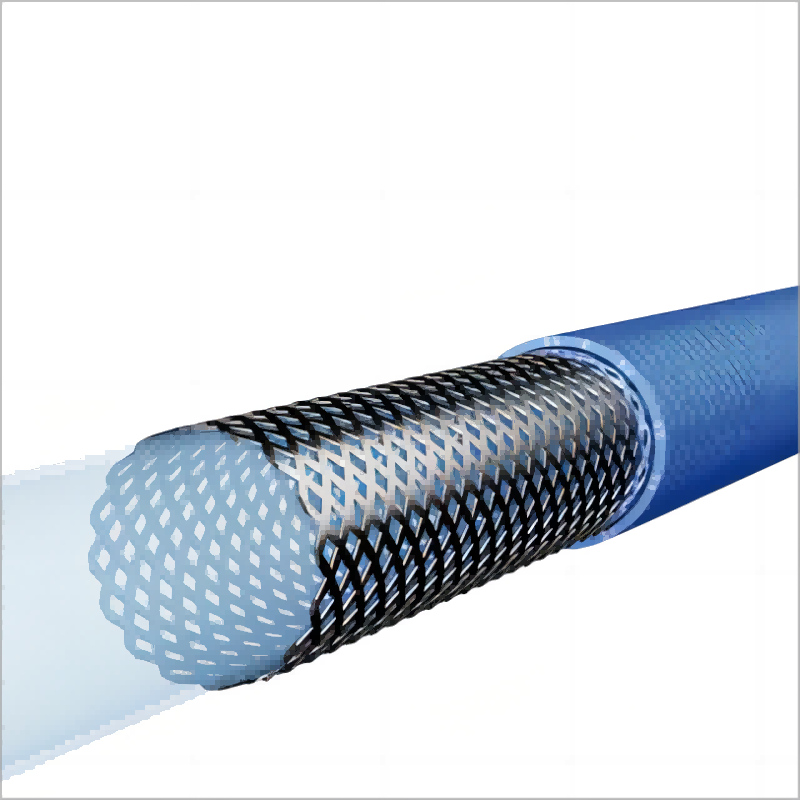
The braid reinforcement is made of a special structure. It uses a middle layer that is made of SUS304, nickel-titanium wire, or stainless steel wire. The wire is round or flat, and it is either braided or made into a spring form. This structure improves the shaft’s tensile strength, making it more durable. It also increases the flexibility of the shaft. One of the main purposes of braid reinforcement is to prevent kinking or deformation when the shaft is under pressure. This feature is especially useful in maintaining the shape and function of the shaft during procedures.
Coil Reinforcement
The coil reinforcement has a different structure. It uses a helical wire that is wound around a central core. This coil structure provides strong support for the shaft. It helps the shaft maintain its shape even when bent. The coil reinforcement is important for providing both high radial strength and flexibility. This ensures that the shaft can withstand pressure while maintaining its function in the medical procedure.
Materials Used in Shaft Construction
Outer Jacket Material
The outer jacket of the endoscopic steerable shaft is made from medical-grade materials. These materials ensure the safety and biocompatibility of the shaft. This helps minimize the risk of any adverse reactions or complications for the patient. The outer jacket is designed to be flexible, smooth, and durable. These properties make it easier to handle and provide better protection for the internal components of the shaft.
Braiding Materials
The middle layer of the shaft is reinforced with specific braiding materials. These materials include SUS304, nickel-titanium wire, and stainless steel wire. The wire can be either round or flat and is braided or formed into a spring shape. The use of these materials enhances the strength and flexibility of the shaft. They help improve the overall performance by adding durability and resistance to external pressure.
Performance and Benefits
Increased Control and Precision
One of the key benefits of the steerable shaft is the improved control it provides. The shaft can navigate through complex anatomical pathways more easily. This increased control helps doctors perform procedures with greater precision. As a result, visualization and targeting are better during endoscopic procedures.
Strength and Durability
The materials used in the shaft construction improve its mechanical strength. This reduces the risk of failure or damage during use. The reinforced structure ensures the shaft remains functional even in challenging conditions, making it more reliable for medical procedures.
Flexibility
Flexibility is another important feature of the steerable shaft. The shaft can adapt to the patient’s anatomy and complex tissue structures. This flexibility is crucial for performing procedures in areas that require careful manipulation and precise movement.
Applications in Medical Procedures
Vascular Interventions
In vascular interventions, the steerable shaft is used to deliver contrast media, saline solutions, or therapeutic agents. It is commonly used in procedures like angiography, angioplasty, and stent placement. The shaft helps guide these substances to the right locations in the body, ensuring the procedure goes smoothly.
Endoscopy
The shaft is also used in various endoscopic procedures. It helps deliver irrigation fluid, suction, or therapeutic agents. For example, it is used during gastroscopy, colonoscopy, and bronchoscopy. The steerable shaft makes it easier for doctors to navigate inside the body and perform these procedures safely.
Urology Procedures
In urology, the steerable shaft is used for similar purposes. It delivers contrast media, saline solution, or therapeutic agents during procedures like cystoscopy, ureteroscopy, and nephrostomy. The shaft’s ability to navigate through small and delicate areas makes it highly useful in these medical interventions.
Surgical Procedures
The steerable shaft is also employed in various surgical procedures. It is used for the delivery of irrigation fluid, suction, or therapeutic agents during operations like laparoscopy, arthroscopy, and neurosurgery. The shaft’s flexibility and steering capability help doctors perform precise surgeries with minimal invasiveness.
Diagnostic Imaging
Finally, the steerable shaft is used in diagnostic imaging procedures. It helps deliver contrast media during imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound. This allows for better visualization of internal structures and helps in accurate diagnosis.
Final Words
The Demax Endoscopic Steerable Shaft with Braid and Coil Reinforcement is a crucial tool in modern medicine. Its medical-grade outer jacket ensures safety and comfort for patients. The braid and coil reinforcements provide exceptional strength and flexibility, allowing precise control during procedures. This design helps doctors navigate complex body areas with ease and accuracy. The shaft’s durability reduces the risk of failure, making it reliable for various medical applications. From vascular interventions to endoscopy and urology, the Demax’s shaft enhances the effectiveness of minimally invasive surgeries. Its balanced design between strength and flexibility makes it a trusted choice for healthcare professionals, improving outcomes for patients.